Difference Between Cacao and Cocoa Plus Health Benefits
May 6, 2022
What is Bean to Bar Chocolate? True Meaning, History, & Process
May 30, 2022Chocolate History Timeline
With Emphasis on Key Events
The history of chocolate is fascinating. From the fatty, bitter drink of the Mayans and the Aztecs over 3000 years ago to today’s yummy melt-in-the mouth chocolate bar or delicious Hot Chocolate, the invention of chocolate is a proof of human ingenuity.
This article records chocolate history through the ages, showing you how the preparation evolved and which personalities played major roles to invent one of the world’s favorite snacks we have today.
If we have to list every detail along chocolate’s history, we’ll provide you with a book! To spare you that pain, we list here the key events in the timeline.
Chocolate History Timeline of Major Events
Pre-Columbian Era – The Mayans and later the Aztecs made a very bitter frothy drink from roasted and crushed cacao beans. The drink, called chocolatl, meaning “bitter water”, was usually spiced with chili pepper and sweetened with bee honey. Considered too stimulating for women and children, it was drunk mostly by men.
About AD 600 – The first known cacao plantation was established by the Mayans in South Yucatan
1502 – Christopher Columbus brought back cacao beans to Europe after his fourth voyage
1519 – The Aztecs introduced the Spanish conquistadors, headed by Hernan Cortés, to the chocolate drink
1527-28 – Hernan Cortés returned to Spain with cacao, recipes, and tools for preparing the drink. He would later introduce the drink to the Spanish court. Sugar was added to the drink by this time
1606 – Chocolate drink reached Italy almost one hundred years after it was introduced in Spain.
1615 – Spanish Princess, Anne of Austria, introduced chocolate to the French when she married Louis XIII. Chocolate became a popular drink in France by 1657 with the marriage of Maria Therese to Louis XIV. As in other areas, it was still a drink for the wealthy.
1657 – A Frenchman opened a shop in London to sell chocolate drink. Chocolate houses soon spread throughout Europe
1670 – Chocolate brought to France from Spain
1690 – Hans Sloane, an Anglo-Irish physician and naturalist, added milk to chocolate beverage to make it more palatable.
Early 1700s – Spaniards planted cocoa trees in Fernando Po, from where cocoa entered West Africa in the late 1800s. Africa would later become the largest producer of cocoa bean as the demand for chocolate increased.
1728 – Fry and Sons began manufacture of chocolate in Bristol, England.
1730—Richard Brookes remarked that chocolate could be eaten in solid form. At this time, chocolate was still consumed only as a beverage.
1753 – Carl Linnaeus named the cacao tree Theobroma cacao.
1756 – First chocolate factory established in Germany.
1776 – Doret invented a hydraulic machine that ground cacao seeds into a paste.
1795 – Joseph Fry installed a steam engine in his chocolate factory in Bristol, England.
1828 – Caspar Van Houten Sr. invented the cocoa press to remove part of the cocoa butter that makes up more than half of the cocoa bean. His son Van Houten Jr. later developed the Dutching process of treating cocoa nibs or cocoa powder with an alkali to produce powders that dispersed and did not sink in a water-based drink. This also resulted in powders with enhanced color and flavor.
1831 – John Cadbury began the production of drinking chocolate and cocoa
“Eating” Chocolate
The creation of cocoa butter led to the discovery that if the butter was milled together with cocoa nibs and sugar, the mixture resulted in a solid chocolate that could be eaten instead of drunk. Cocoa butter held the sugar and cocoa powder together, so the chocolate wasn’t crumbly.
1847 – Joseph Fry established the first British factory to manufacture the world’s first plain eating chocolate in Bristol, UK. They produced the candy bar by mixing cacao butter back into defatted cocoa powder.
1854 – The beginning of Whitman’s boxed chocolates.
1857 – Cacao trees were introduced into Ghana, now one of the leading cacao bean producers in the world.
1867 – Condensed milk developed by the Page Brothers’ Anglo-Swiss Condensed Milk Company in Switzerland.
1875 – Daniel Peter of Switzerland produced the first milk chocolate bar and chocolate tablets, aided by a condensed milk formula developed by Henri Nestlé.
1876 – Daniel Peter introduced a line of milk chocolate designed for eating. At this time, chocolate bars were still ground to make chocolate drinks.
1879 – Rudolf Lindt invented the conche in Switzerland. The conche produced smoother, tastier chocolate, a significantly different texture from Fry’s and Daniel Peter’s gritty chocolate bars. Daniel Peter and Henri Nestlé formed partnership with Rudolf Lindt which later resulted in the formation of the Nestlé Company.
1889 – Freia, a Norwegian chocolate company, founded.
1900 – The beginning of Hershey’s chocolate bar.
1905 – Cacao tree planted in Cote d’Ivoire, who is currently the world’s largest cacao bean producer. That same year, Cadbury Dairy Milk bar was launched.
1906 – Cadbury introduced Bournville alkalized cocoa powder.
1906 – The beginning of Hershey’s Kisses.
1908 – Theodore Tobler created triangular nougat-filled chocolate bar.
1911 – Mars chocolate founded in Tacoma, Washington.
1912 – Beginning of Whitman’s Sampler boxed chocolates
1913 – Jules Suchard invented filled chocolate bonbon
1913 – Creation of Goo Goo Clusters (caramel, chocolate, marshmallow, peanuts). Klein Chocolate Company founded in Pennsylvania.
1915 – Mountain Tacoma bar introduced.
1921 – See’s Candies created in Los Angeles, California.
1923 – Creation of Milky Way bar.
1924 – Valrhona Chocolate established in Tain L’Hermitage near Lyon.
1925 – Mr. Goodbar introduced.
1927 – Welch’s Fudge bar introduced.
1928 – Dreyer’s ice cream established in Oakland. This helped to popularize chocolate through ice cream.
1929 – El Rey chocolate company founded in Venezuela by Jose Rafael Zozaya and Carmelo Tuozzo.
1930 – Nestlé manufactured the first white chocolate from cocoa butter, sugar, and milk powder
1930s – Chocolate used in coating other products or as ingredients in other products. Brands also developed during this period under the same manufacturers’ names.
1931 – Chocolate tempering process developed to control bloom in chocolate molding.
1932 – PayDay bar introduced. Beginning of Three Musketeers bar. Also beginning of Mars Bar (almonds, chocolate).
1936 – Forever Yours bar introduced. Beginning of 5th Avenue bar (peanut butter crunch and chocolate).
1939 – Introduction of Hershey Miniatures.
1940 – Forrest Mars Sr. and Bruce Murrie introduced M & Ms.
1947 – Cluizel Chocolates established in Paris.
1955 – Bernachon Chocolates established in Lyon.
1974 – Marathon bar introduced.
1989 – Symphony milk chocolate bar introduced.
1989 – Milky Way Dark bar introduced.
1992 – Beginning of Dove dark chocolate bar.
1994 – Introduction of Kudos Cookies N Cream bar.
1997 – Scharffen Berger chocolate founded in Berkeley, California.
1997 – Serge Couzigou established Musé e du Chocolat in Biarritz, France.
1998 – Day Chocolate launched Divine, a fair-trade chocolate bar, in England.
2000 – Name of Milky Way Dark bar changed to Milky Way Midnight.
2001 – Beginning of M & Ms Dulce de Leche Caramel Chocolate Candies.
2006 – Development of Mars American Heritage chocolate
2004 – Jacques Torres opened his Chocolate Haven factory and retail store in New York City
Important Milestones and 5 Personalities Who Shaped Chocolate History
Without these names and milestones, we wouldn’t have chocolate as we know it today. These names and events ushered in turning points in making chocolates that today’s chocolatiers continue to build up on.
We present them to you in chronological order.
1. Invention of the Cocoa Press by Van Houten Sr.
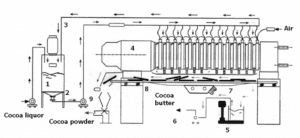
Schematic depiction of a cocoa press [9]. 1: Cocoa liquor conditioning tank. 2: Cocoa liquor pump. 3: Pipe for cocoa liquor. 4: Hydraulic cocoa press. 5: Cocoa butter scale. 6: Cocoa butter pump. 7: Cocoa butter pipe. 8: Cocoa cake conveyor. 9: Cocoa powder milling system.
In 1815, dutchman Van Houten Sr. opened a chocolate factory in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Thirteen years later, in 1828, he invented a manually operated hydraulic cocoa press to make less fatty chocolate drinks.
There were no chocolate bars at that time. Instead, roasted cocoa nibs (shelled cocoa bean cotyledons) were usually milled to produce cocoa mass, which was then mixed with milk to produce chocolate drink or mixed with sugar and flavors to make cookies.
Just how important was this invention of the cocoa press to the industry and chocolate history?
It led to the production of two important cocoa products: Cocoa butter and cocoa powder.
Although this wasn’t the first appearance of cocoa powder, it was the first time where the butter was intentionally pressed out in a factory to make a chocolate drink that was less fatty.
Cocoa mass is made up of about 54% fat. When it was passed through the press, about half of the fat was removed. Later on, the quantity removed from a cocoa press depended on what type of powder was desired.
High fat powders for making drinks – contained about 23% fat content
Low fat powders for making ice creams, cookies, and cakes – about 10-13% fat content
What remained after the required butter was pressed out of the mass was a cocoa cake. This cake would then be ground into cocoa powder.
We shall talk about the importance of cocoa butter in the creation of “eating chocolate” or chocolate bar, but first, let’s see the discovery of the alkalization of cocoa powder.
2. The Dutching Process by Van Houten Jr.
Most people credit one Van Houten for both the invention of the cocoa press and the dutching process, but there were two, father and son.
The father invented the cocoa press, and the son discovered the alkalization of the cocoa cake. What great contributions by one family to chocolate history! The dutching process is so called because it was developed in the Netherlands.
Natural cocoa powder is more likely to form clusters or sink to the bottom in a water-based drink. To disperse the powder, Van Houten treated the powder with an alkali such as potassium carbonate.
Coupled with the importance of the invention of the cocoa press, the major contributions of the Dutching process, to the chocolate industry and history includes:
-Mass chocolate production
-Enhanced color and taste of cocoa powder. Dutched cocoa powder is darker in color and less bitter than natural cocoa powder
-Experimentation with the alkalizing process. This creates cocoa powder of various colors
Solid “Eating” Chocolate
So far, chocolate had been manufactured and consumed mostly as a drink or as ingredient in cookies, cakes, and ice cream.
Then enter a Joseph Fry’s family with the first British factory to manufacture the world’s first solid chocolate bar. That was in 1847.
3. J.S. Fry & Sons and the World’s First Chocolate Bar
With the invention of the cocoa press, chocolate makers needed to find a use for the cocoa butter. But it took nineteen years after the invention before British chocolate makers, J. S. Fry and Sons, made the first chocolate bar in 1847.
By mixing some of the cocoa butter with cocoa powder and sugar, they got a chocolate bar that wasn’t crumbly because cocoa butter helps to hold the solid cocoa particles together in a uniform mixture that melts in the mouth.
The Fry’s chocolate bar was merely a plain block with the basic ingredients. Another milestone was to be made when Henri Nestle developed a condensed milk formula for babies.
4. Daniel Peter
Daniel Peter, a Swiss chocolate maker, invented the first milk chocolate in 1875 by adding powdered milk to chocolate.
The process that started in 1857 was compounded for years because Peter needed to find a way to evaporate the much water in liquid milk to have a product that would last longer.
Fortunately, his neighbor Henri Nestle, developed a condensed milk formula, which meant Peter had less water to evaporate using water-powered machines.
Yet it took another twelve years of finetuning his process before his brand was launched in 1887.
5. Rudolf Lindt
In 1879, Rudolf Lindt, a Swiss chocolate maker, invented the conching process which improved the quality of chocolate.
At the time, most eating chocolate didn’t melt in the mouth well because the solid ingredient particles were not small enough. Chocolate bars were still being ground and melted in hot water for drinking.
To get a smoother, tastier chocolate, Rudolf invented a machine that pushed warm chocolate forward and backward for several days until all particles were finely ground. This allowed the cocoa butter to coat every particle, resulting in a fine smooth chocolate.
The machine was called the conche because of its shape like a shell of the same name.
History of the Chocolate Bar
Below is the timeline of various candy bars produced sometimes as brands under different manufacturers.
1847 – First chocolate candy bar by Joseph Fry and Sons
1905 –Dairy Milk bar by Cadbury
1875 – First milk chocolate bar by Daniel Peter
1915 – Mountain Tacoma bar introduced
1921 – See’s Candies by Charles See, his wife, and his mother
1923 – Milky Way bar by Mars Inc.
1925 – Mr. Goodbar by Hershey Company
1927 – Welch’s Fudge bar.
1932 – PayDay bar. Also Three Musketeers bar and Mars Bar (almonds, chocolate)
1936 – Forever Yours bar. 5th Avenue bar (peanut butter crunch and chocolate)
1939 – Hershey Miniatures by Hershey
1940 – M & M’s by Mars Inc.
1974 – Marathon bar. Changed in 1990 to Snickers, owned by Mars Inc.
1989 – Symphony milk chocolate bar
1989 – Milky Way Dark bar
1992 – Dove dark chocolate bar
1994 – Kudos Cookies N Cream bar
1998 – Divine, a fair-trade chocolate bar
2000 – Milky Way Dark bar changed to Milky Way Midnight
2001 – M & Ms Dulce de Leche Caramel Chocolate Candies
Current Top 10 Chocolate Companies, Their Founding Dates, & Countries of Origin
1911 – Mars, England
1946 – Ferrero spA, Italy
2012 – Mondelez International (Originally Kraft Foods Inc. founded in 1923), USA
2009 – Meiji Holdings Company, Ltd., Japan
1894 – The Hershey Company, USA
1866 – Nestlé S.A., Switzerland
1845 – Lindt and Sprungli, Switzerland
2016 – Pladis (from a merger of United Biscuits, Ulker, Godiva Chocolatier, and DeMet’s Candy Company). Pladis is headquartered in London, UK.
1932 – Glico Group, Japan
1956 – Orion Confectionery, South Korea
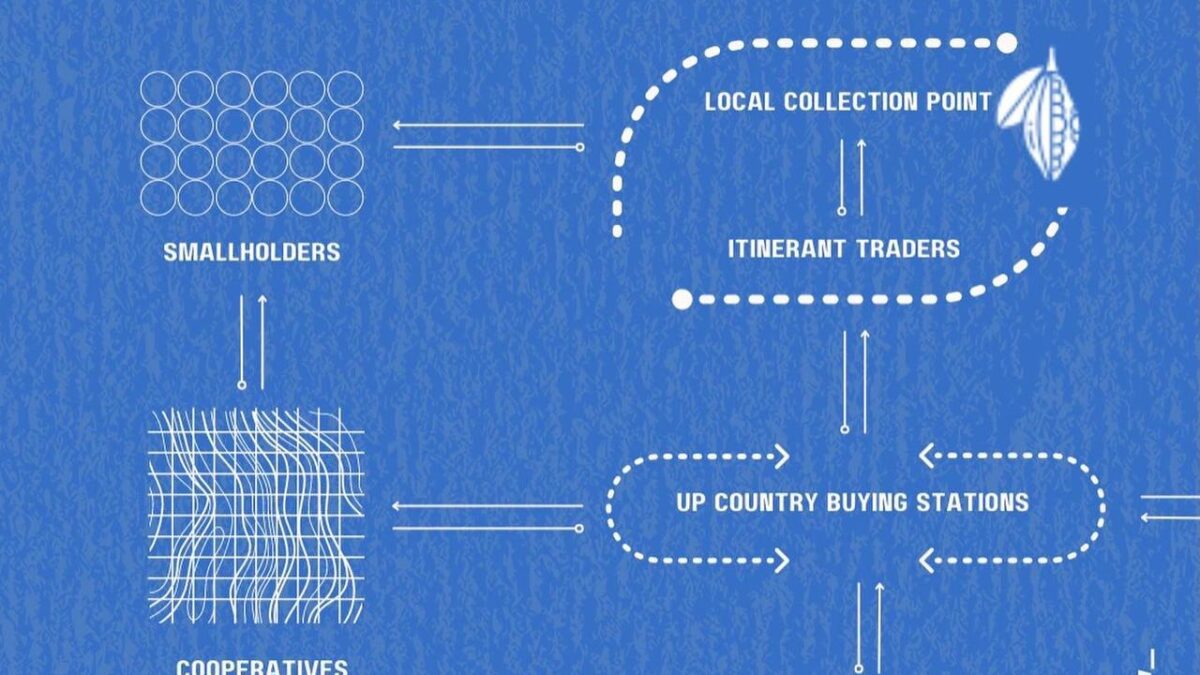
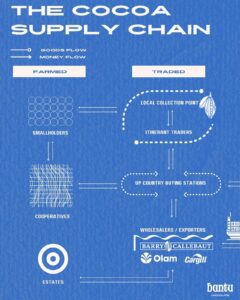
Infographics of the Cocoa Supply Chain and How Chocolate is Made
Some Interesting Facts About Chocolate History
1. July 7 is World Chocolate Day or International Chocolate Day. Some believe it is the anniversary of chocolate’s introduction in Europe in the mid sixteenth century.
2. At the time the Aztecs consumed chocolate as an unpleasant-looking bitter drink, cacao beans were also used as currency.
3. It took about 300 years since chocolate left the Aztec empire to the rest of the world through Spain before chocolate could be considered as food instead of just beverage.
Frequently About Chocolate History
Where did chocolate originate from?
The cacao tree originated from the Americas. The Mayans and Aztecs consumed chocolate as a spicy, bitter drink. When the Spanish took cacao to Europe, developments in the recipes led to the creation of the first chocolate bar in the UK by J. S. Fry and Sons.
When was the first chocolate bar made?
The first solid chocolate bar was invented in 1847 in Britain by J. S. Fry and Sons
Who invented the first chocolate bar?
J. S. Fry and Sons, British chocolate makers created the world’s first chocolate bar in 1847.
Where is chocolate grown?
The cacao tree from which chocolate is made, is grown mostly by four West African nations, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon. Other nations that also produce significant quantities of cocoa beans are Indonesia, Ecuador, Peru, and Brazil.
References
The Science of Chocolate by Stephen T. Beckett
Chocolate: History, Culture, and Heritage, Edited by Louis Evans Grivetti, Howard-Yana Shapiro
www.britannica.com
Chocolate Extinction: Fact vs. Fiction + What Chocolate Lovers Can Do
Chocolate ExtinctionFact vs. Fiction, What Consumers Can Do Share On Facebook Twitter Email Is the world really running out of chocolate? Not really. Currently the global […]
Corporate Chocolate Gifting Ideas to Appreciate Employees and Delight Clients
Corporate Chocolate GiftingHow to Appreciate Employees & Delight Clients Share On Facebook Twitter Email When it comes to corporate gifting, a one-gift-fits-all approach just doesn't cut […]
Cacao Supper Club at Home: Guide to Tasting Chocolate, Cacao Tea, and Pulp Juice
Cacao Supper Club at HomeGuide to Tasting Chocolate, Cacao Tea, and Pulp Juice Share On Facebook Twitter Email Imagine gathering around the table with a few […]